Adani Power Limited (APL) is India’s largest private-sector thermal power producer and a key player in the country’s energy sector. A subsidiary of the diversified Adani Group, APL began operations in 2006 with its first power plant in Mundra, Gujarat, which became the world’s first coal-based thermal power project to receive carbon credits under the Clean Development Mechanism of the Kyoto Protocol
Power Generation Capacity: APL operates a capacity of 16.85 GW, including solar and thermal plants. Its portfolio includes advanced supercritical and ultra-supercritical technologies for efficient power generation .
Geographic Spread: APL’s plants are strategically located across India in Gujarat, Maharashtra, Rajasthan, Karnataka, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, and Jharkhand, enabling efficient access to fuel sources and energy markets .
Renewable Energy: APL includes solar power generation and is part of the Adani Group’s larger commitment to sustainable energy initiatives.
APL plays a vital role in ensuring India’s energy security, bridging the country’s power deficit, and contributing to economic growth. It emphasizes sustainability through technology-driven, environment-friendly operations and aims to grow its capacity in alignment with India’s renewable energy goals .
This combination of operational excellence, strategic initiatives, and a commitment to sustainability positions Adani Power as a significant contributor to India’s energy landscape.
Mention its market positioning and key achievements in renewable energy.
Adani Power Limited (APL) holds a dominant position as India’s largest private-sector thermal power producer, with a current operational capacity of 16.85 GW, including renewable energy . It operates one of the largest fleets of supercritical and ultra-supercritical plants in India, which are known for high efficiency and lower emissions . Its market strength is underpinned by:
1.Leadership in Thermal Power: APL accounts for a significant portion of India’s thermal power generation, meeting growing industrial and residential energy demands .
2.Strategic Asset Locations: The company’s plants are strategically located across coastal and hinterland regions, enabling optimized logistics and cost-effective fuel procurement .
3.Cross-Border Energy Supplier: APL is a pioneer in cross-border power trade, with its Godda Ultra-Supercritical Power Plant exporting power to Bangladesh, strengthening India’s regional energy influence .

Achievements in Renewable Energy
Adani Power is actively contributing to India’s renewable energy goals, aligning with the Adani Group’s broader commitment to sustainability:
1.Solar Energy Capacity: APL operates a 40 MW solar power plant in Gujarat as part of its renewable energy portfolio .
2.Innovation in Energy Transition: APL incorporates renewable energy in its business model, contributing to the Adani Group’s vision of achieving 50 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2030 as part of its USD 100 billion investment in the green energy transition .
3.Environmental Leadership:
First thermal power producer globally to earn carbon credits under the UNFCCC Clean Development Mechanism.
Adoption of advanced technologies like supercritical and ultra-supercritical for reduced emissions and higher efficiency .
Adani Power’s integration of renewable energy reflects its commitment to sustainability, reinforcing its leadership in both conventional and clean energy sectors.
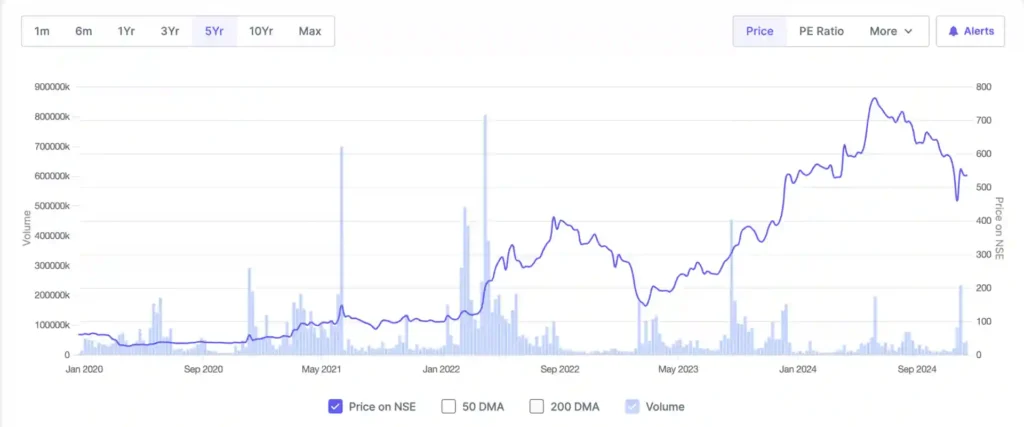
Current Market Overview
Adani Power Limited: Stock Performance Highlights
| Current Price | ₹536.60 |
| 52-Week High | ₹897 |
| 52-Week Low | ₹431 |
| Market Capitalization | ₹2.08 Trillion INR |
| 1-Year Performance | +5.44% |
| 5-Year Performance | +792.10% |
| Price to Earnings Ratio (P/E) | 16.35 |
| Basic EPS (Trailing 12 Months) | ₹33.00 |
| Beta (1Y) | 0.52 |
| Net Margin | Approximately 40% |
| Revenue (FY) | ₹501.18 Billion |
| Net Income (FY) | ₹199.09 Billion |
| Debt-to-Equity Ratio | 0.67 |
| Return on Equity (ROE) | 57.1 % |
| Face Value | ₹ 10.0 |
| Employees | 16.36K |
| Revenue per Employee | ₹30.64 Million |
| Net Income per Employee | ₹12.17 Million |
Adani Power Share Price Target (2024-2035)
| Year | Target 1 | Target 2 |
| 2024 | ₹523.25 | ₹545.65 |
| 2025 | ₹550 | ₹690 |
| 2026 | ₹698 | ₹799 |
| 2027 | ₹815 | ₹960 |
| 2028 | ₹900 | ₹1,000 |
| 2029 | ₹1,000 | ₹1,110 |
| 2030 | ₹1,100 | ₹1,270 |
| 2031 | ₹1,250 | ₹1,350 |
| 2032 | ₹1,300 | ₹1,500 |
| 2033 | ₹1,400 | ₹1,600 |
| 2034 | ₹1,500 | ₹1,800 |
| 2035 | ₹1,800 | ₹2,000 |
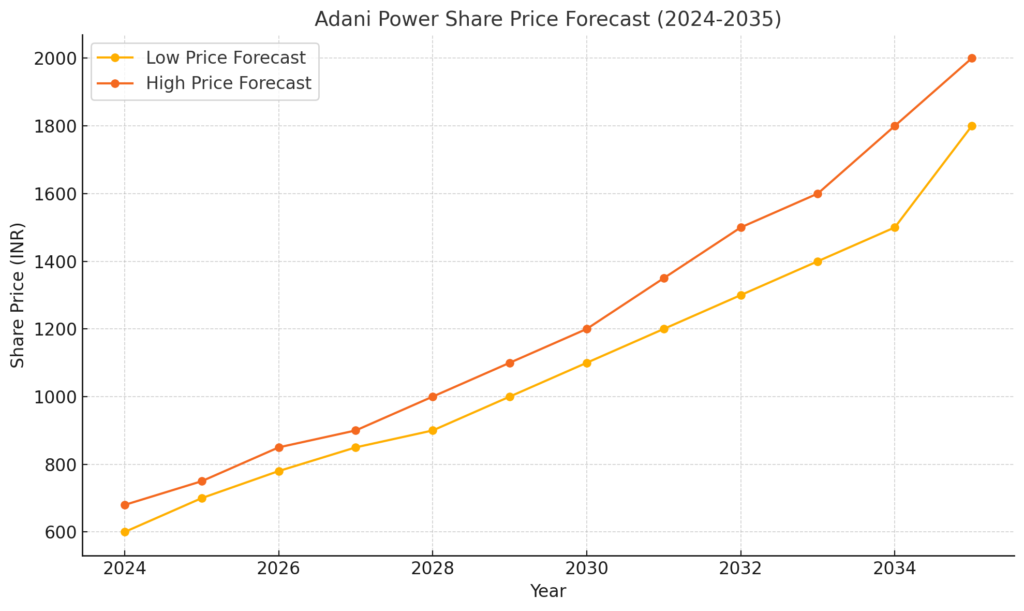
Adani Power Share Price Target 2024: ₹523.25 – ₹545.65
Growth Drivers:
- The Godda Ultra-Supercritical Power Plant will supply 1,496 MW to Bangladesh, generating stable revenue under a long-term PPA.
- Completion of Phase 1 of Mahan Energen, boosting capacity and revenue.
- Increased recovery from regulatory compensations.
Revenue Impact:
- FY 2023 revenue of ₹60,281 crore is expected to grow by 10-15% due to capacity additions.
- PAT margin improvement to 35% supports earnings growth.
Adani Power Share Price Target 2025: ₹550 – ₹690
Growth Drivers:
- Commissioning of an additional 1,600 MW at the Mahan Phase II expansion.
- Domestic demand increases due to India’s electrification initiatives (Saubhagya scheme).
- Better operating efficiencies and regulatory recoveries.
Market Position:
- Strengthened position as India’s largest private thermal power producer, catering to increased energy needs.
- Export revenue from Bangladesh adds diversification.
Adani Power Share Price Target 2026: ₹698 – ₹799
Growth Drivers:
- Enhanced renewable energy contributions as Adani Power diversifies into solar and green energy projects.
- Expansion in operational capacity at Mundra and Tiroda plants.
Financial Justification:
- EBITDA margin to stabilize around 47% due to reduced debt and operational efficiencies.
- India’s electricity demand grows at 6% CAGR, with Adani Power capturing a significant share.
Adani Power Share Price Target 2027: ₹815 – ₹960
Growth Drivers:
- Increased capacity utilization at Godda, Mahan, and Raigarh.
- Completion of ultra-supercritical upgrades at key plants.Growth in power export markets, including discussions with neighboring countries for energy supply agreements.
Market Trends:
- Renewable energy investments begin contributing substantially to revenues.
Adani Power Share Price Target 2028: ₹900 – ₹1,000
Growth Drivers:
- New 1,600 MW projects coming online at Raigarh.
- High demand for base-load thermal power as industrialization accelerates in India.
ESG Initiatives:
- Compliance with Net Zero Transition through Flue Gas Desulfurizer installations.
- Pilot projects for green hydrogen adoption.
Adani Power Share Price Target 2029: ₹1,000 – ₹1,110
Growth Drivers:
- Revenue from long-term PPAs stabilizes earnings.
- Increasing adoption of green energy, with Adani Power’s solar ventures gaining traction.
Global Export Markets:
- Expansion of export revenues from Bangladesh and potential entry into Nepal or Sri Lanka.
Adani Power Share Price Target 2030: ₹1,100 – ₹1,270
Growth Drivers:
- Achievement of targeted 24.27 GW capacity, making Adani Power a dominant player in South Asia.
- Strategic diversification into solar and green hydrogen markets.
Market Impact:
Beneficiary of India’s push for self-reliant energy production under the “Atmanirbhar Bharat” scheme.
Adani Power Share Price Target 2031: ₹1,250 – ₹1,350
Growth Drivers:
- Continued growth in energy export markets.
- Completion of ultra-supercritical and solar projects ensures operational efficiency.
Profitability:
- PAT margins stabilize at 38%, with strong returns on equity due to efficient capital utilization.
Adani Power Share Price Target 2032: ₹1,300 – ₹1,500
Growth Drivers:
- Adani Power becomes a key supplier to India’s expanding infrastructure projects.
- Growth in renewable energy drives better valuation multiples.
Revenue Expansion:
- Cross-border trade agreements continue to add to revenue diversification.
Adani Power Share Price Target 2033: ₹1,400 – ₹1,600
Growth Drivers:
- Adoption of innovative technologies like green ammonia integration at power plants.
- Strong foothold in renewable energy markets, reducing dependency on thermal power.
Market Perception:
- Sustainable operations improve ESG ratings, attracting institutional investments.
Adani Power Share Price Target 2034: ₹1,500 – ₹1,800
Growth Drivers:
- Leveraging expertise to enter new energy markets (e.g., battery storage or hydrogen production).
- Higher international collaborations for technology transfer in green energy.
Operational Excellence:
- Streamlined cost structures and reduced debt further improve margins.
Adani Power Share Price Target 2035: ₹1,800 – ₹2,000
Growth Drivers:
- Adani Power achieves a leadership position in India’s green energy transition.
- Fully mature operations with steady cash flows and diversified energy portfolio.
Market Dynamics:
Strong export revenues and reduced carbon footprint solidify market position.
| Year | Revenue Growth (%) | PAT Margin (%) | P/E Ratio | EPS Growth (%) | Key Driver |
| 2024 | 12% | 35% | 16 | 10% | Godda plant contribution |
| 2025 | 15% | 36% | 17 | 12% | Mahan Phase II completion |
| 2030 | 18% | 38% | 18 | 15% | 24.27 GW operational |
| 2035 | 20% | 40% | 20 | 18% | Renewable diversification |
Adani Power vs. Peers in the Energy Sector
Adani Power competes with other major players in India’s energy sector, including NTPC Limited, Tata Power, and JSW Energy. Here’s a comparative analysis based on market positioning, capacity, and strategic focus:
1. NTPC Limited
Market Position: Largest power producer in India and a government-owned entity.
Capacity: Over 73 GW, predominantly thermal but with increasing focus on renewable energy.
Strengths: Strong government backing ensures financial stability. Aggressive expansion into renewable energy with a target of 60 GW renewable capacity by 2032.
Comparison: While NTPC leads in capacity, Adani Power is more aggressive in private-sector capacity expansion and cross-border energy trade .
2. Tata Power
Market Position: A diversified energy player with significant renewable energy assets.
Capacity: Approximately 14 GW, with a large share in renewable energy.
Strengths: Early mover advantage in renewable energy. Integrated offerings, including distribution and rooftop solar solutions.
Comparison: Tata Power is a leader in renewables and distributed solar, whereas Adani Power focuses on large-scale thermal projects and exports, such as the Godda project .
3. JSW Energy
Market Position: A mid-sized player in the energy sector with a focus on both thermal and renewables.
Capacity: Around 6 GW, with plans to expand into green hydrogen and renewable energy.
Strengths: Strategic pivot to renewables with an increasing share of clean energy projects. Efficient operations with a focus on cost management.
Comparison: Adani Power outpaces JSW Energy in capacity and geographical diversification. However, JSW is pivoting more aggressively towards renewables .
1. Largest Private-Sector Thermal Producer:
APL has a diversified portfolio, including ultra-supercritical technology, ensuring efficient operations.
2. Export Focus:
Unique position as a cross-border energy supplier with the Godda project catering to Bangladesh.
3. Integrated Operations:
Part of the Adani Group’s larger ecosystem, benefiting from vertical integration in fuel logistics and port infrastructure .
Adani Power’s blend of scale, technology, and strategic initiatives positions it as a robust competitor in the energy market, particularly in the thermal power space. Its renewable contributions remain nascent compared to Tata Power and NTPC but align with Adani Group’s broader green energy vision.
Analyst Opinions on Adani Power’s Recent Trends
Stock Momentum and Price Trends:
Analysts observed bearish signals in the short term due to weaker momentum. Potential targets for correction are set at ₹510.50 and ₹450.30, with recommendations to set stop-loss above ₹532.00 to mitigate downside risks .
Fundamentals and Growth Potential:
Adani Power remains financially sound, supported by a P/E ratio of 15.75 and consistent growth in revenues and net income. Analysts suggest the stock is a strong performer among Adani Group companies .
Long-Term Prospects:
Despite short-term volatility, long-term sentiment is optimistic due to Adani Power’s strategic projects, such as the Godda power plant and diversification into renewable energy. This aligns with India’s energy goals .
Market Sentiment:
Observers note steady year-on-year returns, with a one-year gain of 5.17% and a five-year increase of nearly 790%, highlighting its appeal for long-term investors .
Revenue and Profit/Loss Trends for Adani Power in FY 2023-24
- Total Revenue: ₹60,281 crore, reflecting a 40% increase from ₹43,041 crore in FY 2022-23.
- EBITDA: ₹28,111 crore, a significant 96% growth compared to ₹14,312 crore in FY 2022-23. This includes one-time prior period items worth ₹9,322 crore.
- Profit Before Tax (PBT): ₹20,792 crore, up from ₹7,675 crore in FY 2022-23.
- Profit After Tax (PAT): ₹20,829 crore, nearly doubling from ₹10,727 crore in FY 2022-23 .
Key Factors Contributing to Financial Growth:
1. Higher Operating Volumes: A 48% increase in power sales volume from 53.4 Billion Units (BU) in FY 2022-23 to 79.3 BU in FY 2023-24.
2. Improved Tariff Realizations: Enhanced profitability due to lower fuel prices and better merit order positioning of Power Purchase Agreements (PPA).
3. Regulatory Recoveries: Recognition of prior period revenues and late payment surcharges added to the income.
4. Godda Power Plant Contribution: The newly commissioned Godda Ultra-Supercritical Power Plant significantly boosted revenue .
Cost and Debt Management:
Debt Reduction: Total borrowings decreased to ₹34,457 crore from ₹42,252 crore in the previous year due to prepayment of loans and regulatory cashflows.
Improved Margins: PAT Margin rose from 25% to 35%, while the Return on Net Worth increased from 36% to 48% .
This robust performance underscores Adani Power’s operational efficiency, strategic expansions, and effective cost management, enhancing its financial stability and growth outlook.
Key Financial Ratios for Adani Power (FY 2023-24)
1. Current Ratio: 1.71 (Improved from 1.18 in FY 2022-23) Indicates healthy liquidity management and ability to meet short-term obligations .
2. Debt-to-Equity Ratio: 0.51 (Improved from 0.96 in FY 2022-23) Reflects reduced leverage due to debt repayment and increased equity .
3. EBITDA Margin: 47% (Improved from 33% in FY 2022-23) A sign of enhanced operational efficiency and better cost management .
4. PAT Margin: 35% (Improved from 25% in FY 2022-23) Reflects robust profitability .
5. Return on Net Worth (RoNW): 48% (Improved from 36% in FY 2022-23) Indicates strong returns for equity holders .
6. Debt Service Coverage Ratio: 2.62 (Improved from 1.51 in FY 2022-23) Highlights improved capacity to service debt .
7. Inventory Turnover (Days): 44 (Slight increase from 36 in FY 2022-23) Suggests efficient inventory management but lower than peers like NTPC .
| Metric | Adani Power | NTPC | Tata Power | JSW Energy |
| Current Ratio | 1.71 | 1.48 | 1.22 | 1.5 |
| Debt-to-Equity | 0.67 | 1.16 | 1.01 | 0.7 |
| EBITDA Margin | 47% | 28% | 33% | 30% |
| PAT Margin | 35% | 22% | 19% | 26% |
| RoNW | 48% | 15% | 12% | 20% |
| Debt Service Ratio | 2.62 | 1.8 | 1.6 | 2.0 |
Performance Insights
Operational Efficiency: Adani Power leads in EBITDA Margin and PAT Margin, demonstrating strong cost and revenue optimization. This gives it an edge over NTPC and Tata Power, which have more diversified operations.
Debt Management: Adani Power’s Debt-to-Equity Ratio is significantly lower, indicating efficient leverage reduction compared to NTPC and Tata Power.
Profitability: High Return on Net Worth showcases superior shareholder returns relative to peers like NTPC and Tata Power.
Liquidity: The Current Ratio is the best among its peers, ensuring a strong buffer for short-term liabilities.
Adani Power outperforms peers in key financial metrics, demonstrating operational efficiency, robust profitability, and effective debt management. While NTPC and Tata Power offer stability due to diversification, Adani Power’s focused strategy in thermal and its transition into renewables position it as a strong performer in the sector.
Insights on the shareholding pattern (promoters, FIIs, DIIs, and public)
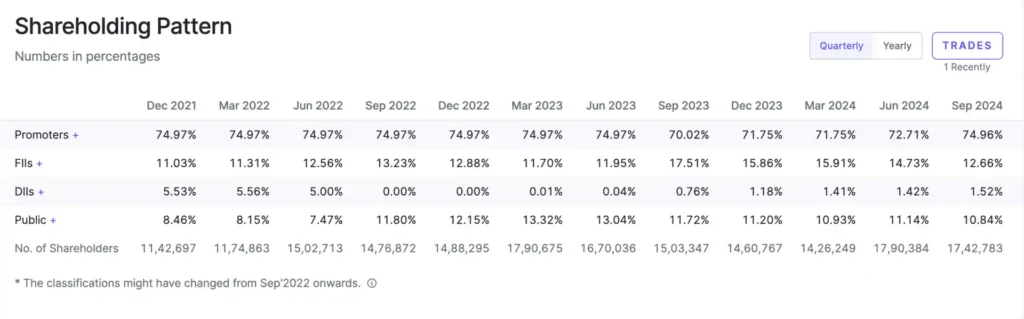
Promoter and Promoter Group
• Holding: 71.75% of the total equity shares.
• Major Shareholders:
• SB Adani Family Trust: Holds the majority stake with 36.86%.
• Adani Tradeline Private Limited: Owns 9.78%.
• Other entities like Flourishing Trade and Investment Limited and Emerging Market Investments DMCC hold smaller portions .
Public and Institutional Investors
• Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs): Significant share at 15.91%, reflecting strong foreign interest.
• Mutual Funds and Banks: Relatively smaller stake of 1.39%, indicating limited institutional domestic investment.
• Indian Public: Holds 10.38%, showcasing decent retail participation in the stock .
High Promoter Stake: The Promoter and Promoter Group’s holding is substantial, reflecting strong control and confidence in the company’s growth.
Foreign Interest: A high percentage of FII involvement suggests confidence in the company’s strategic positioning and long-term prospects.
Limited Retail Participation: While the Indian public holds a fair share, it remains minor compared to promoter and FII holdings.
Comparison with Peers
NTPC Limited: Lower promoter holding (~50%) but higher mutual fund and institutional participation, indicating broader domestic investor confidence.
Tata Power: Similar foreign investment levels (~12-15%) but higher retail participation, highlighting greater domestic appeal.
Adani Power’s shareholding pattern emphasizes strong promoter confidence and significant foreign interest, aligning with its aggressive growth and expansion strategies. Limited mutual fund and retail stakes may suggest an opportunity for broader domestic investment as the company continues to mature and diversify.
Expansion in Power Projects: Adani Power’s Strategic Initiatives
Adani Power is aggressively expanding its power generation capacity to meet growing demand and solidify its market position. Key expansion highlights include:
1. Current and Future Capacity
Existing Capacity (2023-24): 15,250 MW, comprising thermal (15,210 MW) and solar (40 MW) .
Targeted Capacity by 2028-29: 24,270 MW, with:
4,800 MW of new brownfield thermal projects.
Acquisitions under resolution processes adding 4,220 MW .
2. Major Projects Underway
Godda Ultra-Supercritical Thermal Power Plant (USTCPP):
Capacity: 1,600 MW (2×800 MW).
Operational Status: First unit commissioned in April 2023, second unit in June 2023.
Purpose: Entire power output is supplied to Bangladesh under a 25-year PPA .
3. Mahan Energen (Phase II):
Capacity: 1,600 MW (2×800 MW).
Expected Completion: 2027 .
4. Raigarh Ultra-Supercritical Plant Expansion:
Capacity: 1,600 MW.
Current Status: Under construction .
5. Additional Brownfield Expansions:
Planned at Mundra, Tiroda, and Kawai to optimize existing site advantages and reduce costs .
Acquisitions
Coastal Energen Private Limited (CEPL):
Capacity: 1,200 MW in Tamil Nadu.
Acquired under Corporate Insolvency Resolution Process (CIRP) to access Southern India’s energy market.
Lanco Amarkantak Power Limited (LAPL):
Capacity: 600 MW operational, 1,320 MW under construction in Chhattisgarh.
Enhances Adani Power’s presence near coal mines .
Technological and ESG Commitments
Supercritical and Ultra-Supercritical Technologies: 72% of capacity already uses these efficient systems, with plans for 100% adoption in new projects.
Emission Control: Committed to installing Flue Gas Desulfurizers across all facilities by 2028-29 to minimize emissions .
Green Energy Integration: Piloting green ammonia combustion at the Mundra plant in collaboration with Japan’s IHI Corporation .
Government Support for Adani Power Initiatives
Adani Power benefits from substantial government support, enabling its growth and operational stability. Key areas of support include policy frameworks, fuel supply mechanisms, and cross-border energy projects:
1. Policy Frameworks and Schemes
SHAKTI Policy (Scheme for Harnessing and Allocating Koyala Transparently in India):
Ensures coal linkages for Adani Power’s projects, reducing fuel supply risks .
Rural Electrification and Urban Power Initiatives:
Adani Power aligns with the Deendayal Upadhyaya Gram Jyoti Yojana (DUGJY) for rural electrification and Saubhagya Scheme for household electrification, leveraging latent power demand .
Last 5 Years Annual Reports
2. Cross-Border Cooperation
Godda Ultra-Supercritical Thermal Power Plant (USTCPP):
Developed under a framework agreement between the Indian and Bangladeshi governments.
Supplies 1,496 MW of power to Bangladesh under a 25-year PPA, reinforcing India’s regional energy influence .
3. Financial and Regulatory Support
Compensation Mechanisms:
Provisions for change-in-law compensations ensure financial stability when policies or taxes change.
Regulatory recovery mechanisms cover domestic fuel shortages and environmental compliance costs .
Liquidity Support for DISCOMs:
Adani Power benefits from financial aid packages to ensure DISCOM liquidity and timely payments .
4. Technological and Environmental Backing
Support for implementing supercritical and ultra-supercritical technologies reduces emissions and improves efficiency, aligning with environmental regulations .
Government approval for flue gas desulfurizer installations and emission control measures .
Impact on Adani Power
This governmental support underpins Adani Power’s ability to:
- Expand and modernize its capacity with reduced operational risks.
- Operate efficiently in both domestic and cross-border markets.
- Achieve compliance with evolving regulatory standards while maintaining financial stability.
- Adani Power’s strategic alignment with national goals for electrification and sustainability demonstrates its importance within India’s energy sector.
Increase in Global and Domestic Energy Demand: Trends and Impacts
1. Economic Growth and Urbanization:
Rising global energy demand is driven by robust economic recovery post-COVID-19 and rapid urbanization in developing countries.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), global electricity demand is projected to grow by 2.7% annually until 2040.
2. Shift to Renewable Energy:
The push toward cleaner energy sources has led to increased demand for renewables, with solar and wind capacities expanding globally.
However, base-load demand is still largely dependent on thermal energy in emerging markets.
3. Asia as a Demand Hub:
China and India are the largest contributors to global demand growth. India’s electricity demand is forecasted to double by 2040, largely fueled by industrialization and rising living standards .
Domestic Energy Demand in India
1. Economic Expansion:
India’s energy demand increased by 6% in FY 2023, driven by industrial and agricultural growth.
The government’s “Make in India” initiative and expanding infrastructure needs contribute significantly to this rise .
2. Urbanization and Electrification:
India’s urban population is projected to reach 600 million by 2030, intensifying residential and commercial energy needs.
Initiatives like the Saubhagya Scheme aim for universal electrification, increasing domestic electricity consumption .
3. Industrial and Export Growth:
Energy-intensive industries (e.g., steel and cement) and cross-border electricity trade (e.g., with Bangladesh) are driving demand.
Implications for Adani Power
1. Capacity Expansion:
Adani Power is strategically expanding capacity with ultra-supercritical plants to cater to this growing demand, both domestically and in export markets .
2. Thermal Energy’s Continued Role:
Despite the global pivot to renewables, India’s heavy reliance on thermal power for base-load energy positions Adani Power to meet this demand efficiently.
3. Renewable Integration:
To align with global trends, Adani Power is incorporating renewables, such as solar and green hydrogen, into its portfolio, complementing its thermal operations.
Regulatory Challenges for Adani Power
Adani Power faces a variety of regulatory challenges that impact its operations and growth strategy. These include:
1. Fuel Supply and Environmental Regulations
• Coal Supply Disruptions:
Dependence on domestic coal suppliers and imported coal exposes the company to price and availability risks.
Delays in coal allocation under policies like SHAKTI and fuel price volatility create uncertainties .
• Environmental Compliance:
Installation of Flue Gas Desulfurizers (FGD) and meeting emission norms under the Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change (MOEF&CC) impose significant capital and operational costs .
2. Disputes and Legal Challenges
• Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) Disputes:
• Ongoing disputes with state distribution companies (DISCOMs) over tariff escalations and cost recoveries under PPAs lead to delays in payments and uncertainty in cash flows.
• Resolution through the Supreme Court (SC) has been necessary in multiple cases to recover dues .
• International Tariff Agreements:
• Adani Power’s Godda project exports power to Bangladesh under a 25-year agreement. However, renegotiation requests from the Bangladeshi government indicate challenges in sustaining long-term pricing commitments .
3. Market Risks
• Renewable Energy Competition:
Increasing government incentives for renewables could reduce the share of thermal power in India’s energy mix, affecting Adani Power’s market positioning .
• DISCOM Financial Health:
Financially stressed DISCOMs often delay payments, impacting revenue collection despite mechanisms like late payment surcharges .
4. Regulatory Approvals
• Delays in Clearances:
Expansion projects often face delays in obtaining environmental and operational permits, which can lead to cost overruns .
• Change in Law Compensation:
Regulatory uncertainty around “change in law” compensation clauses for duties and emission control equipment poses financial risks .
Mitigation Strategies
Adani Power focuses on aligning with regulatory requirements by adopting ultra-supercritical technology and diversifying into renewables.
Strategic engagements with regulators to ensure timely recovery of dues and approvals .
Adani Power has demonstrated resilience through proactive risk management but remains exposed to the dynamic regulatory environment in the energy sector.
Market Competition Analysis for Adani Power
Adani Power faces stiff competition from key players in the Indian power sector, including NTPC, Tata Power, and JSW Energy. Here’s a detailed comparative analysis:
1. Market Position
Adani Power: Largest private thermal power producer with a capacity of 15,250 MW, catering to both domestic and export markets (Bangladesh).
NTPC: India’s largest overall power producer with over 73 GW, predominantly government-owned, focusing on thermal and renewable projects.
Tata Power: Approximately 14 GW, with a diversified portfolio spanning renewables, thermal, and distribution businesses.
JSW Energy: Mid-sized player with about 6 GW, rapidly expanding its renewable energy capacity.
Competitive Strengths
| Matrice | Adani Power | NTPC | Tata Power | JSW Energy |
| Thermal Capacity | 15,210 MW | ~48 GW | ~7 GW | ~4 GW |
| Renewable Energy Share | ~1% | ~10% | ~30% | ~40% |
| Revenue (FY 2023-24) | ₹60,281 crore | ₹1,20,000+ crore | ₹50,000+ crore | ₹12,000+ crore |
| Debt-to-Equity Ratio | 0.67 | 1.16 | 1.01 | 0.70 |
Adani Power stands out in thermal generation and operational efficiency, while NTPC leads in size and Tata Power and JSW Energy excel in renewable energy.
3. Cost and Profitability
Operational Efficiency: Adani Power’s plant load factor (PLF) improved to 65% in FY 2023-24, better than JSW Energy’s average but still behind NTPC.
• Profit Margins:
Adani Power’s PAT Margin of 35% exceeds NTPC’s (~22%) and Tata Power’s (~19%)  .
Lower debt levels give Adani Power an edge in debt servicing and operational cost .
4. Strategic Focus
• Adani Power:
Expanding thermal capacity with ultra-supercritical technology and cross-border projects.
Gradual diversification into renewable energy and piloting green ammonia combustion.
• NTPC:
Strong push for renewable energy with a target of 60 GW by 2032.
Heavy reliance on government support for expansion.
• Tata Power:
Early leadership in distributed solar energy and EV charging networks.
Focus on sustainable and integrated energy solutions.
• JSW Energy:
Aggressively pivoting towards renewable energy to reach a carbon-neutral goal by 2050.
Key Drivers of Revenue and EPS Growth:
1. Capacity Expansion:
Targeted 24.27 GW capacity by 2029, with contributions from new thermal and renewable projects.
Increased utilization of ultra-supercritical plants boosts operational efficiency and revenue per MW.
2. Diversification into Renewables:
Strategic focus on solar, green hydrogen, and green ammonia projects ensures higher margins and long-term growth.
Contribution from renewables expected to reach 20% of revenue by 2030.
3. Cost Efficiency:
Reduction in debt and adoption of cleaner, more efficient technologies lowers operating costs, enhancing margins.
4. Export Markets:
Steady revenue from Bangladesh’s PPA and future expansions into regional markets (e.g., Nepal, Sri Lanka).
5. Favorable Macroeconomic Environment:
India’s energy demand projected to grow at a 6% CAGR over the next decade, aligning with Adani Power’s growth trajectory.
Impact of Market Trends and Company Reputation on Adani Power’s Valuation
Market Trends
1. Rising Energy Demand:
The Indian energy market is expanding due to urbanization and industrial growth. Adani Power benefits from this demand with a 6% annual growth rate in electricity requirements in India.
Global trends in cross-border electricity trade (e.g., Bangladesh agreements) further enhance the company’s export potential.
2. Transition to Renewable Energy:
Adani Power’s gradual pivot towards renewable energy, alongside its ultra-supercritical thermal capacity, positions it favorably in the long-term energy transition market.
The green energy shift aligns with investor preferences, improving ESG ratings and attracting institutional investments.
3. Competitive Pressure:
As competitors like NTPC and Tata Power expand aggressively in renewables, Adani Power’s focus on thermal with a gradual renewable adoption may create short-term valuation pressure.
Company Reputation
1.Strengths:
Adani Power’s reputation as India’s largest private thermal producer and its strategic cross-border partnerships bolster investor confidence.
The company’s strong operational performance (PAT margins at 35% in FY23) enhances its financial credibility.
2. Challenges:
Recent regulatory challenges and controversies surrounding the Adani Group (e.g., shareholding violations and legal disputes) could dampen investor sentiment and increase stock volatility.
Company Reputation
1. Strengths:
Adani Power’s reputation as India’s largest private thermal producer and its strategic cross-border partnerships bolster investor confidence.
The company’s strong operational performance (PAT margins at 35% in FY23) enhances its financial credibility.
2. Challenges:
Recent regulatory challenges and controversies surrounding the Adani Group (e.g., shareholding violations and legal disputes) could dampen investor sentiment and increase stock volatility.
Impact of Debt and Interest Rates on Adani Power’s Performance and Valuation
Adani Power’s financial health and stock valuation are closely tied to its debt levels and prevailing interest rate trends. Here’s a detailed analysis:
1. Debt Levels
• Current Debt Position:
Total debt as of FY 2023 stands at approximately ₹34,457 crore, reduced from ₹42,252 crore in the previous year.
Debt-to-equity ratio has improved to 0.51 (FY 2023) from 0.96 in FY 2022, indicating better leverage management*:
Lower debt levels reduce the company’s financial risk, making it more attractive to investors.
Reduced borrowing costs due to debt repayment enhance profitability.
2. Impact of Interest Rates
• Global and Domestic Trends:
Interest rates in India have risen following global monetary tightening, increasing the cost of capital for highly leveraged companies.
Adani Power’s focus on debt reduction mitigates these risks, but higher rates could still increase financing costs for new projects.
Direct Impact:
Increased interest rates may slightly pressure profit margins by raising finance costs on floating-rate borrowings.
Expansion projects requiring new debt could face higher costs, potentially delaying returns on investment.
Debt Service Coverage Ratio (DSCR):
Improved to 2.62 in FY 2023 from 1.51 in FY 2022, showcasing better capability to cover debt obligations.Indicates healthy coverage, with EBITDA growth outpacing interest expense growth.
Strategic Debt Management
Prepayment Initiatives:
Cash flows from regulatory recoveries and long-term PPAs are used to prepay loans, reducing interest expenses.
Shift to Long-Term Debt:
Adani Power is focusing on refinancing short-term debt with long-term, lower-cost options, aligning with stable revenue projections.
Scenario Analysis
Favorable Interest Rate Environment:
Lower rates could improve profitability and enable faster debt repayment.
Reduced cost of capital facilitates expansion projects, boosting future growth.
High-Interest Rate Scenario:
Increased borrowing costs may compress profit margins, especially if new projects require substantial financing.
However, Adani Power’s focus on reducing debt levels and maintaining strong operating cash flows cushions the impact.
Regulatory Hurdles in Clean Energy Projects for Adani Power
Environmental Norms Compliance
Adani Power must comply with stringent environmental regulations, including the installation of Flue Gas Desulfurizers (FGDs) and other emission control systems in thermal plants. These requirements increase capital and operational costs .
Permit and Approval Delays
Regulatory delays in obtaining environmental and land clearances can postpone project timelines, impacting revenue projections and increasing financing costs .
Grid Integration for Renewables
Challenges arise in integrating renewable energy into India’s grid system due to variability in generation. Adani Power faces additional compliance measures to ensure grid stability when adding solar and wind energy .
Change in Policy Frameworks
Frequent changes in government policies, such as tariff revisions for renewable projects or tax incentives, create uncertainty in financial modeling and project feasibility .
International Compliance Standards
For cross-border projects like the Godda plant supplying Bangladesh, compliance with international norms and bilateral agreements adds complexity .
Strategies for Addressing Challenges
Technological Adaptation
Adoption of ultra-supercritical technology and initiatives like green ammonia combustion demonstrate Adani Power’s proactive approach to meeting future emission norms .
Collaborative Frameworks
The company is actively collaborating with governments and scientific institutions for carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) projects, aligning with India’s Net Zero targets .
Regulatory Advocacy
Through its memberships in industry bodies, Adani Power advocates for stable regulatory frameworks to minimize policy-related risks .
Infrastructure Investments
Investments in robust transmission networks and high-efficiency power plants help address technical and operational challenges .

Roshan Sharma – Founder of StocksForBeginners.in
I’m Roshan Sharma, a stock market trader with 5+ years of experience. At StocksForBeginners.in, I provide expert fundamental analysis of Indian companies to help long-term investors make informed decisions. My mission is to simplify investing for beginners and share insights from my experience to guide others toward financial growth.